This Week’s Sky at a Glance, 2026 Feb 14 – Feb 21
This Week’s Sky at a Glance, 2026 Feb 14 – Feb 21
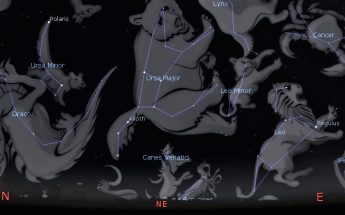
Let’s pay attention to the minority this week. By this I mean the Minor constellations: Ursa, Canis and Leo, all of which are now visible in the evening. Ursa Minor, the Little Bear, hosts the Little Dipper asterism and it has what is arguably the most important and famous star of the night sky–Polaris, the North Star–at the tip of its tail. Although smaller and less bright than the nearby Great Bear, Ursa Minor is at the centre of action in our night sky. How many have heard or even believe that Polaris is the brightest star in the night sky? It actually ranks at number 48.
Canis Minor, the Little Dog, is noted for having the eighth brightest star, Procyon. An imaginary arrowhead formed by Orion’s head and shoulder stars points eastward to the Little Dog. We usually see it as just two stars so it is probably a wiener dog. Despite the brilliance of its luminary, the Little Dog is just the opening act for Canis Major and its leading star, Sirius, the brightest one of the night sky. In early winter Procyon rises first to announce the impending arrival of Sirius, hence the name which means “before the dog.”
Leo Minor the Little Lion experiences difficulty in being noticed, and with good reason. It is one of those inconspicuous constellations created by the 17th century astronomer Johannes Hevelius to fill gaps in the sky. We see it as a triangle between the back of Leo and the feet of Ursa Major. To give it some distinction and pride we can imagine the lion cub nipping at the heels of the Great Bear to keep it from attacking Leo.
This Week in the Solar System
Saturday’s sunrise is at 7:26 and sunset will occur at 5:50, giving 10 hours, 24 minutes of daylight. Next Saturday the Sun will rise at 7:15 and set at 6:00, giving 10 hours, 45 minutes of daylight.
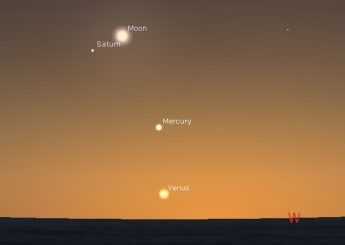
The Moon is new on Tuesday, and the razor-thin lunar crescent sits just below Mercury on Wednesday. The Moon is near Saturn on Thursday with Mercury two binocular fields to their lower right and Venus below it setting around 6:45 pm. Jupiter shines brightly high in the east in early evening, and on Tuesday telescope users can see its moon Europa disappear behind the planet at 7:19 while the Red Spot is in mid-transit. Rural observers might catch the zodiacal light angling up the ecliptic 60 to 90 minutes after sunset early in the week.
Tune in to the Sunday Night Astronomy Show at 8 pm on the YouTube channel and Facebook page of Astronomy by the Bay.
Questions? Contact Curt Nason at nasonc@nbnet.nb.ca.